
Does CBD Treat Depression?
Cannabidiol – often abbreviated as CBD – is a truly remarkable, powerful molecule of the cannabis plant that has dozens of potential health benefits in
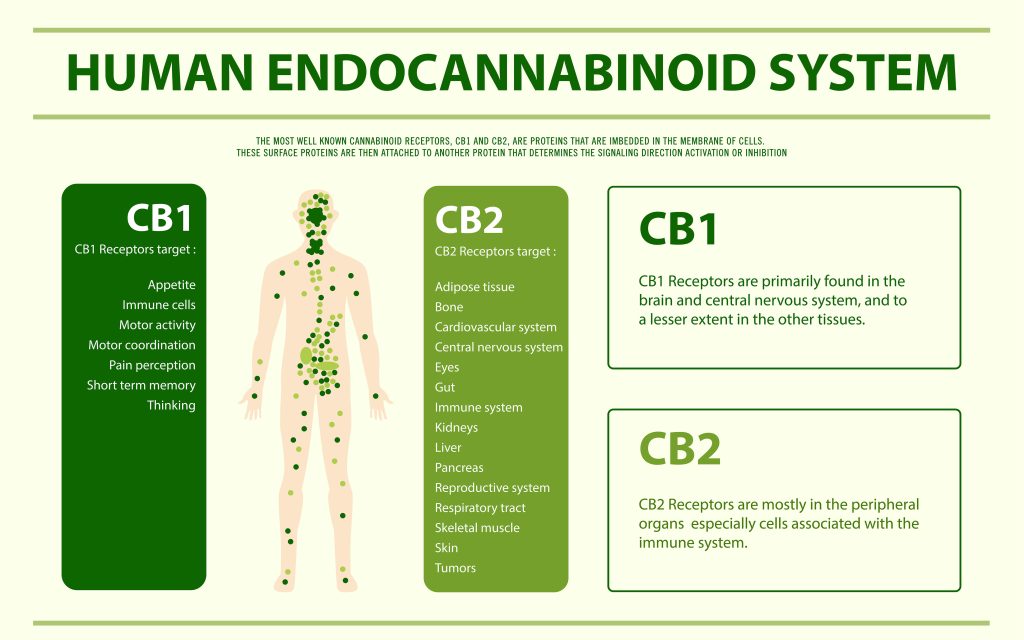
Even if you’re not a regular cannabis user, you’ve probably heard of the two most widely-consumed and extensively researched cannabinoids: tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD).
However, in fact, there are dozens more cannabinoids – the term used in the scientific literature to refer to the set of unique molecular compounds that only occur in the cannabis plant – beyond CBD and THC.
So far, scientists have isolated more than 100 naturally-occurring cannabinoids in total, with potentially even more left undiscovered as of 2022. Adding even more complexity to the cannabinoid landscape, chemists now regularly synthesize new cannabinoids in lab settings, opening the door to potentially limitless innovation in the field.
Due to the nuanced differences in their molecular structures, each of these cannabinoids interacts in unique ways with the human endocannabinoid system (ECS).

image source: Adobe Stock
As a result, they offer up distinct potential health benefits to users.
Here, we’ll explore 4 of the lesser-known cannabinoids that will likely make waves in the upcoming years as researchers learn more about their potential therapeutic applications:
As a minor cannabinoid (which means it’s active but present in relatively low concentrations in cannabis), THC-V (tetrahydrocannabivarin) has never garnered the same intensity or amount of interest from clinical researchers as THC or CBD.
Nonetheless, even given the dearth of scientific scrutiny, we do know that THC-V offers multiple documented potential health benefits, including:
Let’s survey a few of the possible medical benefits, based on clinical research, that THC-V might offer to relieve numerous health conditions:
Although it’s not the predominant cannabinoid in any strain, THC-V is most heavily concentrated in sativa strains like Durban Poison and Malawi.
One of THC-V’s primary benefits for many users is that it doesn’t have the same psychoactive properties as its more common cannabinoid cousin, Delta-9 THC (the one that’s still federally illegal and currently illegal in the state of Georgia as well).
CBG (cannabigerol) is another minor – yet noteworthy – cannabinoid often dubbed the “mother of all cannabinoids” because, as the cannabis plant matures, CBG fosters the synthesis of other, more prominent cannabinoids like CBD and THC.
CBG naturally occurs in low concentrations, but, by using one of the two methods below, cultivators can extract high levels of CBG:
Much like CBD, CBG exerts no psychoactive effects. However, the two cannabinoids act on the ECS in dramatically different ways.
Here are some of the unique potential health benefits that CBG offers based on what we know about how it interacts with the ECS:
Cannabinol (CBN) is an up-and-coming cannabinoid. It does, unlike the other two cannabinoids, possess some psychoactive properties like THC, but they are not significant enough to trigger a “high” unless it’s ingested in extremely large quantities.
CBN concentrations increase in cannabis as the plant ages as THC oxidizes and consequently slowly converts to CBN.
Let’s survey a few of the potential medical benefits that CBN might confer:
To harness the dual combined power of CBG and CBN, check out Sympleaf’s new 600mg CBN + CBD Oil

Delta-10-Tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta-10-THC) is an isomer of THC. (An isomer is one of a pair of compounds with identical molecular content but with different arrangements of their atoms.)
Delta-10 THC rarely occurs naturally in the cannabis plant, although, like, CBN, it has been observed to form as a degradation product in an aging cannabis plant.
Delta-10 THC is more commonly:
Like Delta-8 THC, Delta-10 THC is psychoactive but significantly less so than the more common Delta-9 form of THC (the numbers reference the location of the double-bond on respective carbon atoms).
Also, like Delta-8, Delta-10 THC has become popular among cannabis enthusiasts eager for a legal alternative to the federally banned Delta-9 molecule.
Its effects are very similar, but, again, less potent, than Delta-9 THC, including inducing the trademark “high” of THC that many users are looking for. Delta-10’s effects are often likened to those of sativa strains, which are described as “energizing” and “invigorating.”
Delta-10 is legal at the moment in most states, including in Georgia, but legal battles are underway that might change this status over time.
Staying on top of the latest developments in the rapidly evolving space of cannabinoid research is what we do. To learn more about the four under-appreciated cannabinoids we’ve discussed here, don’t hesitate to contact Sympleaf.
Educational outreach is part of the work we do to serve our Atlanta-area neighbors.
While you’re here, don’t forget to browse through the bevy of independent lab-certified CBD, Delta-8 THC, and CBD products available at the Sympleaf online store.

Cannabidiol – often abbreviated as CBD – is a truly remarkable, powerful molecule of the cannabis plant that has dozens of potential health benefits in

Alzheimer’s disease (AD) – along with a host of other neurodegenerative conditions that impact brain health – is nothing short of a public health catastrophe

To date, CBD (“cannabidiol” in long-form) is the single most potent cannabis compound that researchers have isolated to research its potential health benefits. Here, we
Made in Atlanta. © FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION (FDA) DISCLOSURE These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.